Nick Goold
Understanding the economic indicators that drive currency movements is essential for successful forex trading. One of the most important of these is the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI). PMI reports give traders valuable insight into business conditions and act as a barometer of economic health. Because they influence investor sentiment, interest rate expectations, and global trade flows, PMI readings can have a direct impact on currency exchange rates. This article explains what PMI indicators are, why they matter, and how they move the forex market.
What is the PMI?
The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is a leading economic indicator that measures business activity in both the manufacturing and services sectors. It is based on monthly surveys of purchasing managers—those responsible for ordering raw materials and overseeing supply chains. They are asked about new orders, output, hiring, supplier deliveries, and inventories.
PMI results are published as an index ranging from 0 to 100. A reading above 50 indicates economic expansion, while a reading below 50 signals contraction. Because it reflects current conditions and future expectations, PMI is considered one of the most reliable forward-looking indicators of economic health.
How PMI impacts the forex market
1. Exchange Rate Movement
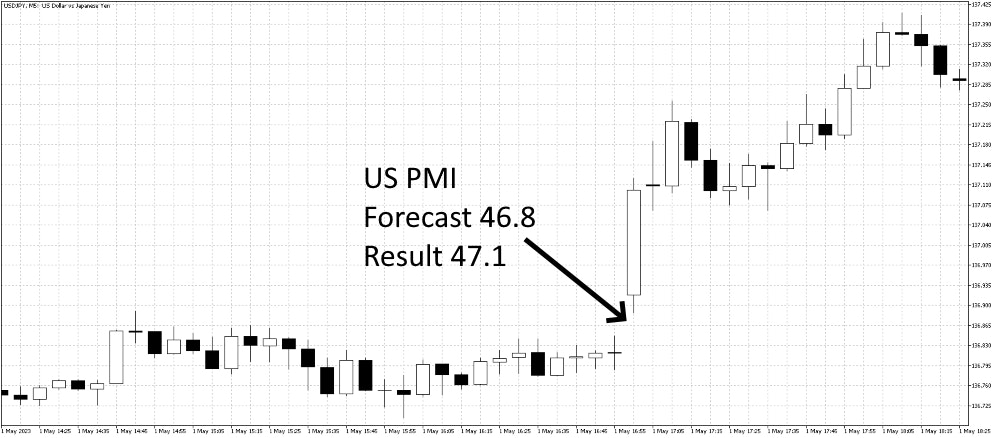
Stronger-than-expected PMI readings suggest that an economy is growing, which boosts investor confidence and increases demand for that country’s currency. As a result, the exchange rate tends to appreciate. On the other hand, weaker-than-expected PMI results point to slowing growth, reducing demand for the currency and often causing depreciation.

2. Interest Rate Expectations
Central banks use PMI data to guide monetary policy decisions. A strong PMI can signal that the economy is heating up, raising the risk of inflation. In response, central banks may raise interest rates, which usually attracts foreign capital and strengthens the currency. Conversely, weak PMI data may encourage rate cuts, which can put downward pressure on the currency.
3. Investor Sentiment and Risk Appetite
PMI is also tied to global risk sentiment. Positive PMI data encourages “risk-on” behavior, where investors move into higher-yielding currencies and assets. Weak PMI readings often spark “risk-off” flows, with traders favoring safe-haven currencies such as the U.S. dollar (USD), Japanese yen (JPY), and Swiss franc (CHF).
4. Global Trade and Commodity Prices
Since PMI reflects demand for goods and services, it also influences global trade and commodity prices. Export-heavy economies tend to see their currencies rise when PMI signals stronger demand abroad. Commodity-linked currencies (like the Australian dollar and Canadian dollar) can benefit from rising PMIs, which point to stronger demand for raw materials. Likewise, weaker PMI readings can weigh on commodities and the currencies of exporting nations.
Key PMIs and release schedules
PMI data is released monthly by various organizations, and forex traders closely track these releases because they can trigger sharp moves in exchange rates. Below are some of the most important PMI releases for major economies:
United States (ISM):
Manufacturing PMI – released on the first business day of each month.
Services PMI – released on the third business day of each month.
Eurozone (S&P Global):
Manufacturing PMI – first business day of each month.
Services PMI – third business day of each month.
Composite PMI – third business day of each month.
China (Caixin):
Caixin Manufacturing PMI – first business day of each month.
Caixin Services PMI – around the fifth business day of each month.
Japan (Jibun Bank / S&P Global):
Manufacturing PMI – first business day of each month.
Services PMI – fifth business day of each month.
United Kingdom (S&P Global / CIPS):
Manufacturing PMI – first business day of each month.
Services PMI – third business day of each month.
Composite PMI – third business day of each month.
Germany & France (S&P Global):
Manufacturing PMI – first business day of each month.
Services PMI – third business day of each month.
Composite PMI – third business day of each month.
Australia (Judo Bank / S&P Global):
Manufacturing PMI – first business day of each month.
Services PMI – third business day of each month.
In addition to these, many other countries release their own PMI data. Together, these reports create a global snapshot of economic conditions and help traders anticipate shifts in the forex market.
Conclusion
PMI indicators are among the most powerful tools for forex traders. They influence exchange rates, shape interest rate expectations, affect global risk sentiment, and even move commodity-linked currencies. By tracking PMI data from the U.S., Eurozone, China, Japan, and other major economies, traders can gain an edge in predicting market moves.
However, PMI should not be used in isolation. The best trading strategies combine PMI readings with other economic indicators (such as GDP, inflation, and employment data), as well as technical analysis and risk management. For forex traders, PMI offers a critical piece of the puzzle when navigating today’s fast-moving currency markets.

